
CODICE is not just a resource planning tool, but the key to maximizing efficiency and adjusting costs. If you want a presentation of our products and services, give us the following information here.
CODICE is not only a public transport planning tool and now also the planning of electric vehicles, but the key to maximising efficiency and adjusting costs. CODICE:
CODICE AIR TRAFFIC CONTROL is a state-of-the-art computer system for the optimal management and planning of associated human and technical resources that ideally solves the planning of air traffic controllers in air navigation service providers CODICE ATC, allows to ensure optimal coverage of control needs, complying with the complex labor regulations that apply in the air navigation sector.

Customers using CODICE for public transportation planning.
The three fundamental elements of any planning scenario are: activity, the room needs to be covered, the air traffic controllers and the rules that prevail in planning.
CODICE gives the planner the freedom to define the room needs for each period of time. In addition, it is an open system that allows defining for each work center which are the profiles on which to define the needs, and in this way the system can be used both in control centers and in single-position towers.
Cost reduction is a critical objective in all organisations and in general in public transport planning. However, schedules must be assigned to people. CODICE’s optimization engine makes it possible to reconcile these two seemingly opposite worlds, obtaining highly efficient planning while taking into account the well-being and preferences of employees.
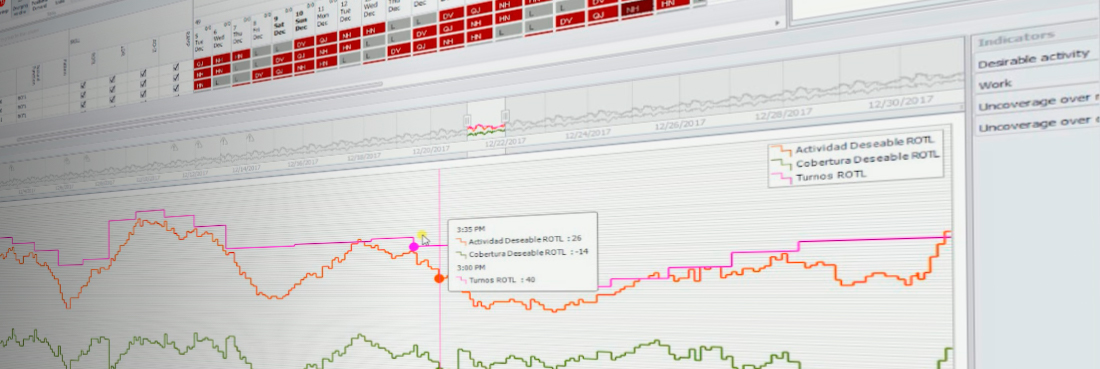
CODICE brings the planner closer to the quality indicators that really matter, providing the key analyzes updated in real time. As important aspects of planning as being sure that all the service is assigned, being sure that you are complying with labor regulations and being aware of the productivity of the planning.
Not all the casuistry that can be presented can be covered by automation, for this reason CODICE makes available to the planner powerful tools to be able to manually modify the planning. These tools greatly facilitate the work of the planner by guiding him according to the circumstances towards the best decision. Thus, for example, the system can suggest the best candidate to receive overtime, it allows to exchange shifts with a click or to recover previous shifts of a resource by eliminating a planned absence period.
Identify the optimal amount of resources you will need to meet long-term forecast demand
Plan your workforce within weeks of its entry into operation
Cover last minute drops or unforeseen demand swings before trading begins.
Exploit the information once the operation is complete
[elementor-template id=”6157″]
[elementor-template id=”6171″]
[elementor-template id=”6174″]
[elementor-template id=”5866″]
[elementor-template id=”5886″]
This module makes it possible to integrate the planning information obtained with CODICE with the operating aid system. This integration operates on two levels: